Many people enter the forex market with dreams of quick profits, only to be swept up in a whirlwind of conflicting signals and unpredictable moves. If you want to last in this game, you need more than luck—you need the structure and insight that technical analysis (TA) brings. This technique is not a fleeting or theoretical idea; instead, it’s an organized and systematic approach to measuring price movements. While fundamental analysis looks at macroeconomics, TA focuses on charts, past performance, and statistical valuation. In the ultra-volatile forex environment, where developments provoke instant responses, a systematic approach to market analysis is highly beneficial. This guidebook will give you a solid foundation in TA’s core concepts. We’ll show you the basic tools and, more importantly, how to use them to build your trading strategies with confidence and clarity.
Understanding the Core Concepts of Technical Analysis
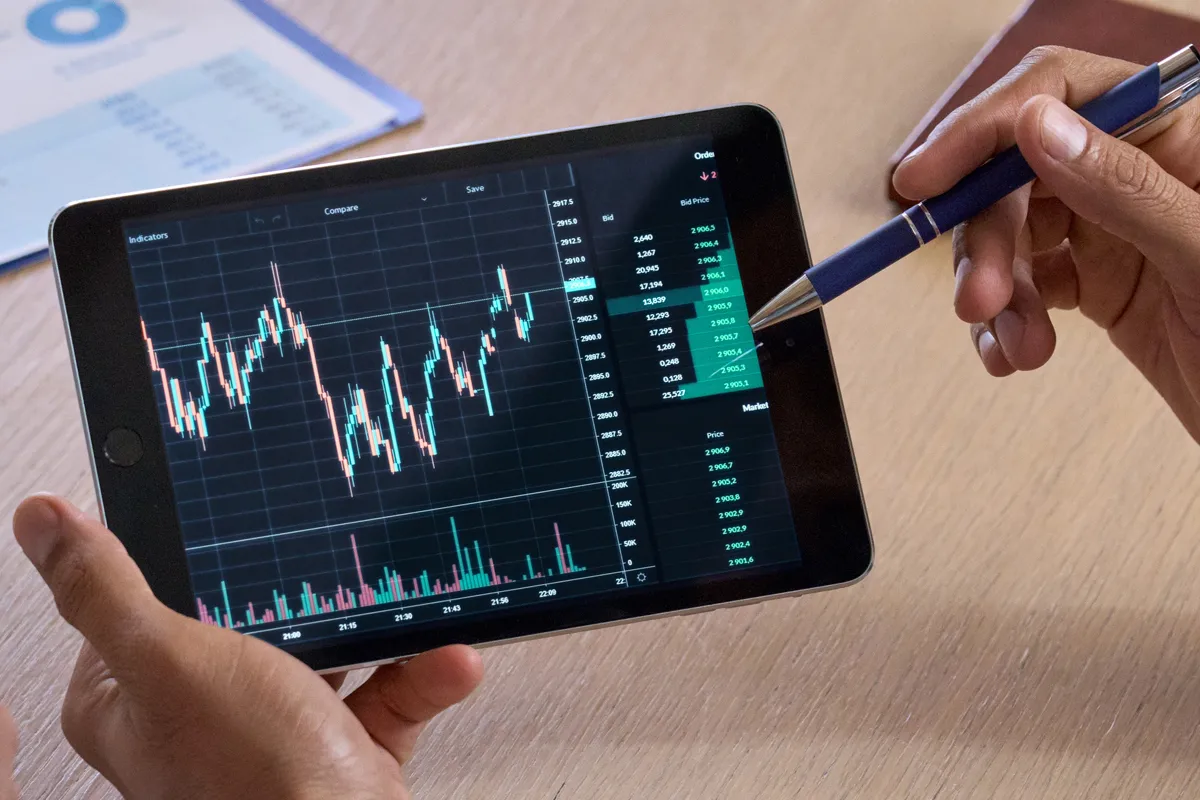
The first assignment for beginners is to learn the skills to read a forex chart and perform technical analysis. While bar and line charts are sound alternatives, candlestick charts are usually preferred. Candlestick charts are a favorite because they tell a whole story in a single bar. You can quickly see the opening, high, low, and closing prices for any period. By reading these formations, you can spot trends, gauge momentum, and even predict potential reversal points—all of which help you understand the battle between buyers and sellers. The candlestick’s body shows you the price difference between the open and close, while its wicks (or shadows) mark the highest and lowest points reached.
The Underlying Basis of TA
This understanding leads to a significant question: What is the underlying basis of technical analysis in forex trading? Technical analysis is a systematic approach to evaluating investments. It aims to discover potential future trade opportunities by analyzing statistical patterns related to trading activity. These patterns include price movements over periods of rises and declines, as well as changes in trading volume.
Applying Technical Analysis in Trading
Next, a relevant question is: How is technical analysis applied in forex trading? Traders use technical analysis to determine the best times for entering and leaving positions. They use the study of charts to select proper time frames for making trades, set stop-loss levels to manage risk better, and identify the best opportunities for realizing a profit. Think of technical analysis as your personal trading guide. It’s what keeps your emotions in check, so you’re not just chasing every market move. Instead, you get to lean on data and proven strategies, steering clear of the emotional traps that so often trip up traders.
Technical vs. Fundamental Analysis
A frequent question among new traders relates to the difference between technical analysis (TA) and fundamental analysis (FA). TA is concerned with prior price action and chart patterns. FA, on the other hand, looks at the big picture. It focuses on interest rates, employment data, and significant world events, from elections to political upheaval.
The smartest traders combine both approaches. They use fundamentals to spot the long-term direction, and technical analysis to nail down the perfect entry and exit points. For example, a retail trader can see a strong GDP report as a reason for a bullish long-term view (FA). They can then use a technical level to plan an entry strategy that is effectively risk-reducing (TA).
Reliability and Limitations of Technical Analysis
Now, a crucial question arises: Can technical analysis predict forex market movements? The simple answer is no. Its purpose is to help you anticipate potential movements based on historical patterns and market psychology, not to predict the future with 100% certainty. It’s about aligning your trades with the most probable outcome. Therefore, the question is, how reliable is technical analysis in forex? How well this works comes down to your skill, discipline, and risk management. Appropriately used, technical analysis can be incredibly effective.
But it’s not flawless—it can’t account for the unpredictable ways human emotions can move the market. It also can’t account for every unforeseen major news event that could cause a sudden, dramatic price shift. In choppy, sideways markets, technical analysis can send false signals. That’s why it’s always wise to confirm what you see with other tools before making your move.
Understanding Basic Market Levels and Trends
Proficiency in technical analysis requires a thorough grasp of its underlying tenets. The trend concept takes precedence; it captures the overall direction of the market. A trend can be either an uptrend, where the market makes a series of higher highs and higher lows, or a downtrend, where it consistently makes lower highs and lower lows. A horizontal market movement is a third option.
Support and Resistance: Finding Key Zones
Support and Resistance concepts are also essential. They are areas where past price actions have traditionally found reversals or stops. For forex traders, identifying these levels involves analyzing specific regions where prices have consistently interacted before reversing. These points represent a high concentration of buyers, thereby supporting the market while also creating resistance for sellers.
Although traders usually represent these pivotal levels as horizontal lines, the best description is as zones. Price reversals rarely take place at the same points. After spotting these levels, traders apply them directly to their trades. For instance, they might buy near a strong support level or sell near resistance. This is a foundational strategy that both new and veteran traders use.
Price Action and Trendlines
While support and resistance give you a map of the market’s key zones, understanding the direction and flow of the price is the next step. This is where trendlines and the concept of price action come into play. They help you visualize the market’s story and find potential entry points, even without relying on complex indicators.
The Role of Trendlines
A common question is: What is the function of trendlines within forex analysis? Traders use trendlines to outline and visually verify the direction of a trend. They draw a rising trendline between a series of successively higher lows, while a declining trendline joins a series of successively lower highs. The trendlines represent a simple but effective tool for identifying potential market entry points or points for a trend reversal.
Price Action: Reading the Chart’s Story
Another question is, what sets price action trading apart? Traders who focus their analytical setup on the shifting of prices revealed on charts usually favor this specific approach. They purposefully avoid using technical indicators. Traders who take this approach have a better understanding of price movement in key levels, allowing them to read market stories through candlestick charts. In most cases, price action traders attempt to recognize distinct candlestick patterns or formations located near specified support and resistance levels to confirm trading sentiments.
Tools, Patterns, and Platform Essentials
As you grow in experience, you’ll encounter more advanced concepts and tools. Candlestick patterns are a great example. Patterns like hammers, Dojis, or engulfing setups tell a story about market mood. They can hint at momentum changes, possible reversals, or upcoming breakouts, giving you extra confidence in your trade setups.
Common Candlestick and Chart Patterns
The concept that relates to chart patterns in forex trading, including head and shoulders and double top patterns, falls into this category. These specific arrangements within a chart often indicate a potential continuation or reversal of an existing trend. The head and shoulders pattern, for example, represents a trustworthy reversal indicator. A double top pattern reveals the weakening of an uptrend. The ability to recognize these common patterns becomes an essential competency for a technical analyst.
Multi-Time Frame Analysis
Another popular question is, “What’s the right time frame for technical analysis in forex?” The right chart time frame depends on your style. Day traders often work with 15-minute or 1-hour charts to catch fast moves, while swing traders prefer 4-hour or daily charts for longer trends. This mix of perspectives is the core of multi-time frame analysis—one of forex’s most useful concepts. The strategy entails a trader looking at a larger time frame (e.g., the daily) to identify the current trend, then zooming in on a smaller time frame (e.g., the 1-hour) to find an entry point. Using this strategy helps avoid making trades opposite the current trend, hence significantly increasing your chances of success.
Essential Trading Platforms
Begin your research by thoroughly understanding the software or platforms used for technical analysis in the foreign exchange market. When you’re ready for a platform, MT4 and MT5 are the go-to choices—they’re reliable, robust, and loaded with features. TradingView has also become a favorite for its sleek charts, easy interface, and lively trading community. Between them, you’ve got everything you need to draw trendlines, use indicators, and analyze charts like a pro.
Closing Thoughts
The value of consistency and emotional control outweighs the use of a particular strategy or tool. While technical analysis provides a systematic approach, it still depends on the trader to apply the strategy with precision and dedication. Don’t think of technical analysis as a short-term trick. See it as a marathon—a long-term process that demands continuous learning, practice, and adaptability.
Start with a demo account on a reliable platform. Practice what you’ve learned, review your past trades to spot trends in your behavior, and keep a trading journal. It’s the best way to build your practical skills and awareness. Use technical analysis as a tool for understanding market functions rather than for a head-on confrontation. Traders who take intentional action within the trading environment can anticipate positive results. Commit to a balanced strategy as it applies to technical analysis, as no one method can ensure success. However, it is one of the strongest tools available to traders for skilled navigation.